The Ultimate Guide to Pain Killer Pills: Your Comprehensive Resource
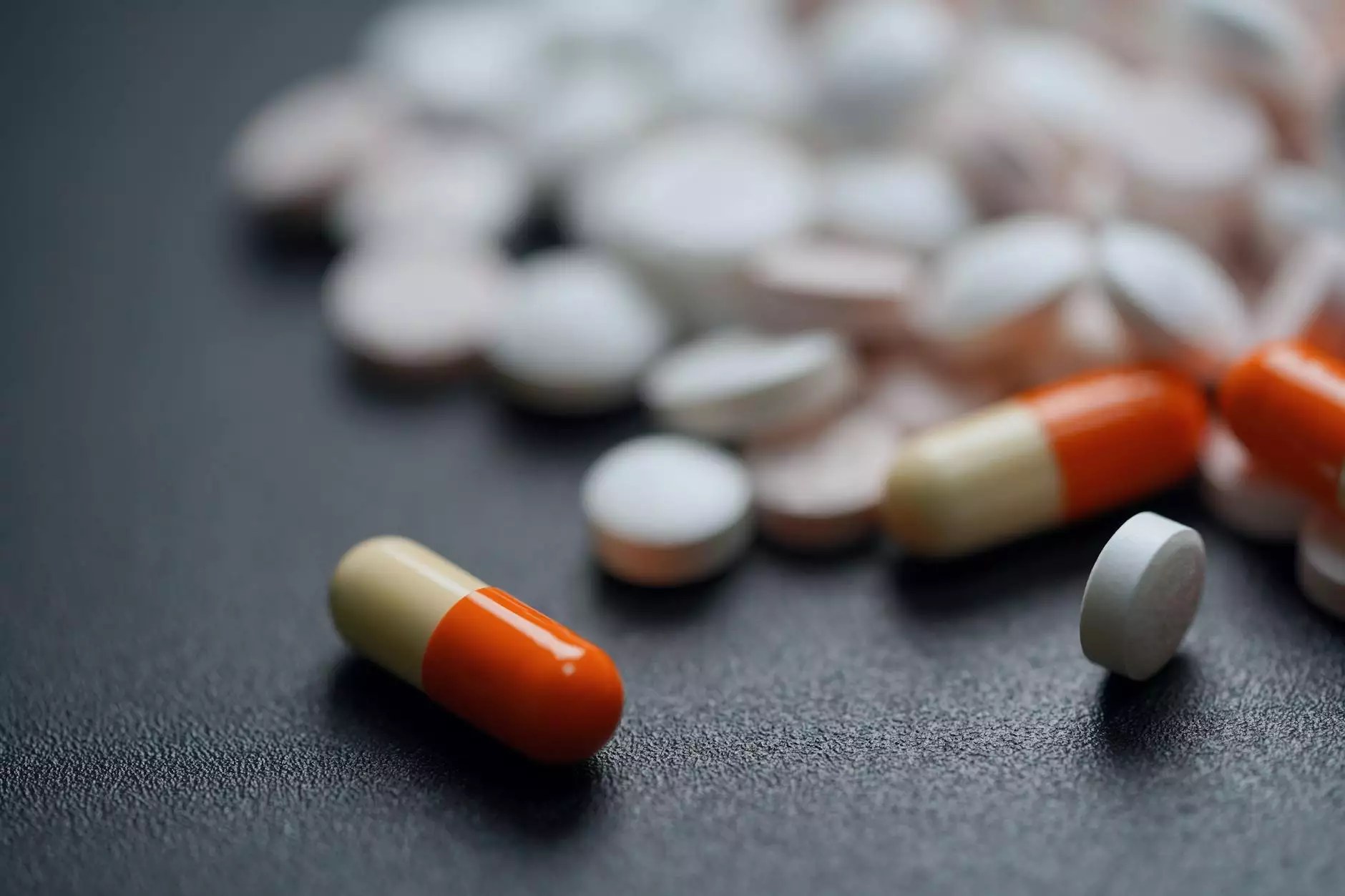
In today's fast-paced world, pain management is a critical aspect of maintaining a high quality of life. Whether due to chronic conditions, injuries, or postoperative recovery, many individuals seek solutions to alleviate discomfort. Among the most common solutions are pain killer pills, which offer relief to millions around the globe. This article will delve into the various types of pain relievers, their mechanisms, benefits, potential side effects, and best practices for usage.
Understanding Pain: A Brief Overview
Pain is a complex experience that can manifest in various forms, from sharp and acute to dull and chronic. The body's pain response serves as a warning system, alerting us to injury or illness. Understanding the types of pain is essential, as it often guides treatment decisions. Here are some categories:
- Acute Pain: This type of pain is sudden and often severe, typically resulting from injury, surgery, or illness.
- Chronic Pain: Lasting for months or longer, chronic pain continues even after the underlying cause has resolved. Conditions like arthritis and fibromyalgia fall into this category.
- Neuropathic Pain: Arising from nerve damage, this type of pain can lead to sensations such as burning, tingling, or numbness.
Types of Pain Killer Pills
There are several categories of pain killer pills, each working in distinct ways to provide relief. Understanding these categories is crucial for choosing the most effective treatment.
1. Non-Opioid Pain Relievers
These medications are commonly used for mild to moderate pain relief and include:
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol): Often used for headaches, muscle aches, and fever, acetaminophen works by inhibiting pain signals in the brain.
- Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): This group includes ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) and naproxen (Aleve). NSAIDs reduce inflammation, which can help relieve pain caused by injuries or conditions such as arthritis.
2. Opioid Pain Relievers
For moderate to severe pain, opioid medications may be prescribed. These include:
- Codeine: Though lower in potency, codeine is effective for relief from mild to moderate pain.
- Morphine: A powerful analgesic commonly used in medical settings for severe pain treatment.
- Hydrocodone and Oxycodone: Often combined with acetaminophen, these medications provide significant pain relief but come with a risk of dependence.
3. Adjuvant Medications
These medications can enhance the effects of pain killers or serve as primary treatments for certain pain types:
- Antidepressants: Certain antidepressants, such as amitriptyline, are effective for nerve pain management.
- Anticonvulsants: Medications like gabapentin and pregabalin are used to treat nerve pain and help stabilize electrical activity in the brain.
How Pain Killer Pills Work
Understanding the mechanism of action of pain killer pills can empower patients to make informed decisions. Here’s a brief overview:
Non-Opioid Mechanisms
Non-opioid pain relievers typically target the prostaglandins, chemicals in the body that promote inflammation and pain. By inhibiting the enzymes responsible for their production, these medications reduce both pain and inflammation.
Opioid Mechanisms
Opioids work by binding to specific receptors in the brain, spinal cord, and other areas of the body. This interaction blocks pain signals and alters the perception of pain, providing significant relief for severe discomfort.
Benefits of Pain Killer Pills
The primary benefit of pain killer pills is their effectiveness in relieving pain. However, the advantages extend beyond simple discomfort relief:
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Effective pain management allows individuals to engage in daily activities, work, and enjoy personal relationships.
- Improved Functionality: Managing pain can significantly improve mobility and independence, especially in those with chronic pain conditions.
- Support in Recoveries: After surgery or injury, pain medications play a vital role in recovery, enabling patients to participate in rehabilitation efforts.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
While pain relief medications are beneficial, they also come with risks and potential side effects. Being informed is crucial:
Risks Associated with Non-Opioid Pain Relievers
Non-opioid medications can lead to symptoms like gastrointestinal distress, liver damage (especially with excessive acetaminophen), and increased bleeding risk with NSAIDs. It's essential to follow dosage instructions closely.
Risks Associated with Opioid Pain Relievers
Opioids carry a higher risk of dependence, addiction, and overdose. Side effects can include drowsiness, constipation, and respiratory depression. Therefore, they must be prescribed with caution and monitored regularly by healthcare professionals.
Best Practices for Using Pain Killer Pills
To maximize the benefits and minimize risks associated with pain killer pills, consider the following best practices:
- Consult Your Doctor: Always discuss your pain with a healthcare professional who can recommend appropriate medications and dosages.
- Use as Directed: Adhere to prescribed dosages and administration schedules to prevent complications.
- Monitor Your Symptoms: Keep track of your pain levels and any side effects to inform your healthcare provider during follow-up visits.
- Avoid Mixing Medications: Combining different pain relievers, particularly opioids and alcohol, can lead to serious health issues.
Alternative Pain Management Options
In addition to pain killer pills, various alternative strategies can help manage pain effectively:
- Physical Therapy: Engaging in guided exercises can strengthen the body, improve flexibility, and reduce pain.
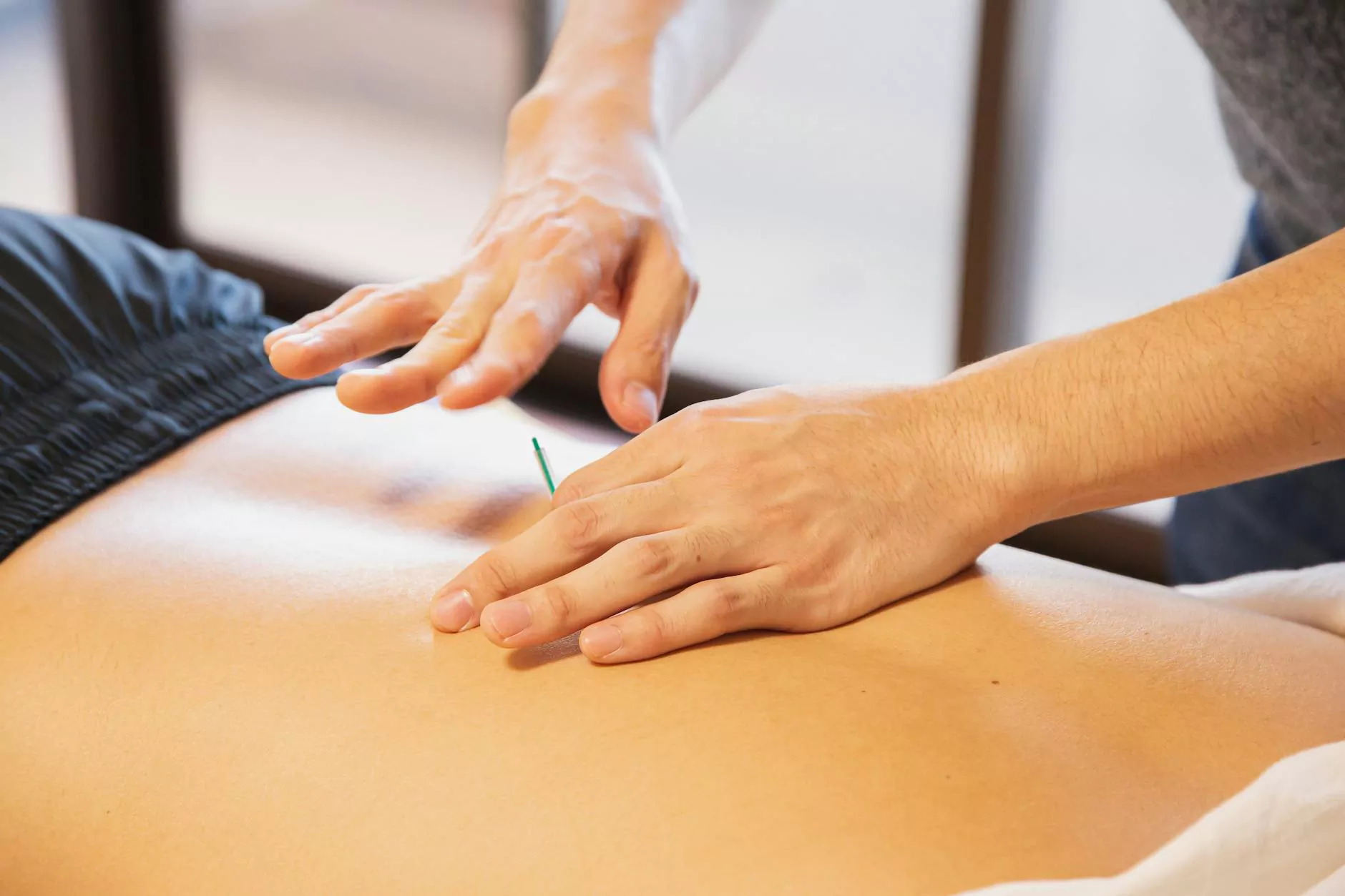
- Acupuncture: This traditional practice involves inserting needles at specific points to alleviate pain.
- Mind-Body Techniques: Practices such as meditation, yoga, and biofeedback can help individuals manage pain through mental and physical mindfulness.
Conclusion
Pain killer pills are a fundamental component of pain management strategies for many individuals suffering from various types of pain. By understanding the different types of pain relievers, their mechanisms, benefits, and potential risks, patients can make informed choices about their treatment options. It is always advisable to consult with healthcare providers to formulate a safe and effective pain management plan tailored to individual needs. With the right approach, achieving a pain-free life is within reach, helping you to enjoy all that life has to offer.